Real Life Examples of a Continuous Variable
Continuous Variable is a type of variable in Mathematics and Statistics. A variable is referred to as a numerical expression whose value varies. There are only two types of variables namely the Continuous variable and the Discrete variable. A continuous variable can be defined as a numerical variable whose value is attained by measuring. These variables can take any type of numeric value and can be divided into further relevant smaller increments such as fractional and decimal values. A continuous variable is a kind of quantitative variable that is frequently used in machine learning and statistical modeling to describe data that is measurable in some way. Continuous variables are measured on scales such as height, temperature, weight, etc.
Key Terms: Continuous Variable, Discrete Variable, Variable, Statistics, Mean, Median, Variance, Real Number, Calculus
What is a Continuous Variable?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A continuous variable is one whose value can be derived by measuring and so has an uncountable set of values. Continuous variables are those that have an endless number of values and exist between any two numeric values. For example, a variable over a non-empty range of real numbers is continuous if it can take on any value in that range. As a result, the real number range between x and y with x, y ∈ R, and x ≠ y; is said to be uncountable and infinite.
Continuous variables, such as height, weight, and temperature, are typically measured using scales. Continuous variables can be used to calculate mean, median, variance, and standard deviation.
In continuous optimization applications with continuous variables, many calculus approaches are applied. In statistical theory, the probability distributions of continuous variables can be stated in the form of expressions of probability density functions.
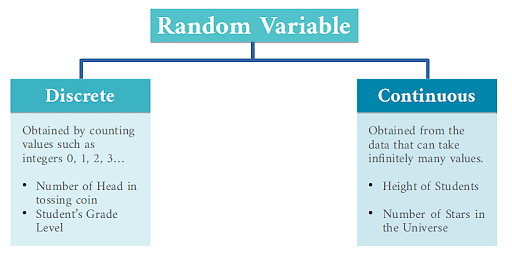
Types of Variable
Do Check Out:
Types of Continuous Variables
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are two types of continuous variables:
- Instant Variable: Instant variables are those that specify the level or distance between each equal and static category. For example- the temperature is Fahrenheit.
- Ratio Variable: The ratio variable is another sort of continuous variable. This variable differs from interval variables in just one way. The only distinction is that the ratio of the scores indicates the link between the responses. For example- the height, weight, and age of a person.
Read More: Continuous Function
Characteristics of Continuous Variables
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some characteristics of continuous variables are
- Continuous variables are often not counted.
- The values may be broken into smaller and smaller bits, each with its significance.
- Continuous data may be measured.
- Within an interval, it has an endless number of potential values.
- Histograms and scatterplots are graphical representations of continuous data
Difference Between Discrete Variables and Continuous Variables
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A discrete variable is a statistical variable that presupposes a finite collection of data and a countable number of values. In contrast, a continuous variable is a quantitative variable that accepts an endless collection of data and an uncountable number of values.
- The range of a discrete variable is full, but the range of a continuous variable is not.
- Counting can be used to get the values of discrete variables. Continuous variables, on the other hand, are random variables that measure something.
- Discrete variables are assumed to have independent values, whereas continuous variables are assumed to have any value within a certain range or continuum.
- Isolated points can be used to depict a discrete variable visually. In contrast, a continuous variable may be represented on a graph using linked points.
- For the discrete variable, non-overlapping or mutually inclusive categorization, when both the class limit is included, is appropriate. On the other hand, given a continuous variable, overlapping or mutually exclusive categorization, in which the upper-class limit is excluded, is applicable.
Read More: Mean and Variance of Random Variable
Examples of Continuous Variables
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Here are a few examples of continuous variables:
- The duration of time needed to finish a project.
- The height of a child.
- The time required to sell a pair of shoes.
- The volume of rain that pours in a storm in inches.
- A two-bedroom house's square footage.
- The mass of a vehicle.
- Car acceleration.
Read More: Discrete Mathematics
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- In Mathematics, a variable can be classified into two types namely a Continuous variable and a Discrete variable.
- Continuous variables can have an infinite number of values between the lowest and highest measurement points.
- Speed and distance are considered examples of continuous variables.
- Continuous data are ideal for inferential statistics, but they are less effective for data mining and are typically stored as discrete data or sets.
- Logic levels are used to transfer a continuous variable onto a discrete binary variable.
Previous Year Questions
- Find the Variance of the given table … (BITSAT 2013)
- The Variance of first 50 even natural Numbers … (JEE Mains 2014)
- Standard Deviation of first n odd numbers … (KEAM)
- If the greatest angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is 3 times the least angle, then the radian measure of the least angle is…. (COMEDK UGET 2005)
- Of all open tanks in the form of a rectangular parallelopiped with a square.base having a fixed volume, the one that has the least inner surface area has the property that its... (COMEDK UGET 2005)
- The standard deviation of the first n natural numbers is... (JKCET 2008)
- All the students of a class performed poorly in Mathematics. The teacher decided to give grace marks of 10 to each of the students. Which of the following statistical measures will not change even after the grace marks were given?...(JEE Mains 2013)
Sample Questions
Ques. Give an example of a continuous variable. (3 Marks)
Ans. The height of a person is an example of a continuous variable. Assuming that the person has the most precise measuring instrument in the world, one that allows measuring heights to whatever decimal point we choose.
Assume that a person is between 150 and 153 cm tall, however, we want to know his/her exact height. The gadget reads 150.3 cm to the first decimal place. To two decimal places, it equals 150.31 cm. There are an unlimited (or infinite) number of alternatives between 150 cm and 153 cm: 150.45, 150.99999, 152.543.
Ques. X is the length of an arm picked at random. Tell whether X is a discrete or continuous random variable. (1 Mark)
Ans. X is a continuous random variable. The length of a person's arm can vary continuously. All possible lengths cannot be listed.
Ques. A student rolls a dice several times. The number X represents the number of rolls required until the student rolls a 6. Tell whether X is a discrete or continuous random variable. (3 Marks)
Ans. A random variable is discrete if the set of values it takes is finite, or can be organized as a list. For example, a random variable that takes only whole-number values is always discrete.
A continuous random variable is a random variable that is not discrete. A random variable that can vary continuously, or, in other words, can take any value in an interval, is continuous. X is a discrete random variable. The number of rolls needed is always a whole number.
Ques. Is the average number of goals scored a continuous or discrete variable? (3 Marks)
Ans. The (unrounded) average of a collection of whole numbers is always regarded as a continuous variable: while it can never be an irrational number, it may also be so many potential rational values that modeling it as a discrete variable is impracticable.
Ques. Is mass continuous or discrete? (3 Marks)
Ans. Since mass may have any value between its lowest and maximum, it is a continuous variable. Mass is not discrete since there is no definitive response to the question: What is the next mass figure following, say, 40.207 Kg?
Ques. Is systolic blood pressure continuous or discrete? (3 Marks)
Ans. In theory, an individual's systolic blood pressure is a continuous variable since it can range between 0 and 300 mmHg. Systolic blood pressure, as recorded by a monitor, is a discrete variable since it can only take on different values, such as 140 mmHg, 141 mmHg, and so on.
Ques6. What are the few characteristics of continuous variables?(3 Marks)
Ans. A few characteristics of continuous variables are:
- The values may be broken into smaller and smaller bits, each with its significance.
- Continuous data may be measured.
- Within an interval, it has an endless number of potential values.
- Histograms and scatterplots are graphical representations of continuous data
- They are represented by connecting the points on the graph.
Ques. What are some differences between a discrete and continuous variable?(3 Marks)
Ans. Some differences between discrete and continuous variables are as follows:
| Basis of Comparison | Discrete Variable | Continuous Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A discrete variable has a limited number of isolated values. | A continuous variable may take on an unlimited number of possible values. |
| Range of Specified Number | Complete | Incomplete |
| Values | Counting is used to get values | Values are obtained by measurement. |
| Assumption | Distinct or different values | Any value between the two possibilities. |
| Representation | Graphical Lone Points | Linked Points |
Check-Out:
Source: https://collegedunia.com/exams/continuous-variable-definition-types-characteristics-and-examples-mathematics-articleid-6707
0 Response to "Real Life Examples of a Continuous Variable"
Post a Comment